Introduction
Bacterial Meningitis is a condition that is quite serious and affects the brain as well as the spinal cord. It is due to the infection of certain blah blah blah by bad bacteria.If you do not treat this condition immediately, it can turn dangerous and endanger life. In this blog, we will try to put all this complex medical terms into the simplest of words. You will discover what actually happens to it in terms of cause, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Particular regions of the world have a high rate of bacterial meningitis incidences. These regions are mostly those with poor health facilities. It is important, however, to understand this disease, for quite often an early diagnosis can save a life. All ages can suffer from this disease, but babies, toddlers, and the elderly are mostly at risk.

What is Bacterial Meningitis?
Bacterial meningitis is the infection of the meninges-hence covering the brain and spinal cord. The infection causes inflammation that could end up being detrimental and serious. Unlike viral meningitis, bacterial meningitis is more serious, and you should seek medical attention without delay.
When bacteria enter the bloodstream, they can quickly migrate to the brain and spinal cord. In other cases, the bacteria might be able to infect the meninges by travelling through ear infections, head injuries, or surgical procedures. The pressure exerted on the brain from inflammation of the meninges leads to the following life-threatening symptoms.
Causes of Bacterial Meningitis
Bacteria cause this type of meningitis, and the following are some of the most common bacterial agents.
Streptococcus pneumoniae: This bacterium is the single most common etiology for bacterial meningitis in children as well as adults and generally follows ear infections or pneumonia.
Neisseria meningitidis: This is spreads through respiratory droplets and usually affects closely congregated groups, like dorms and military camps.
Haemophilus influenzae: caused more than 80% of meningitis cases in children before the Hib vaccination became available.
This bacteria commonly exists in contaminated food products like dairy and processed meats and usually affects born infants, pregnant women, and older people.
Escherichia coli (E. coli): Typically acquired from mother at parturition; these bacteria are more prevalent in newborns.
By what means bacteria are disseminated?
Different ways are used to disseminate bacteria causing meningitis. They include:
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Kissing/getting in close contact.
- Sharing forks, spoons, drinks, or toothbrushes.
- During the process of birth, transmission from mother to baby.
Living in crowded conditions, being immunocompromised, or being unvaccinated may increase the risk of getting bacterial meningitis.
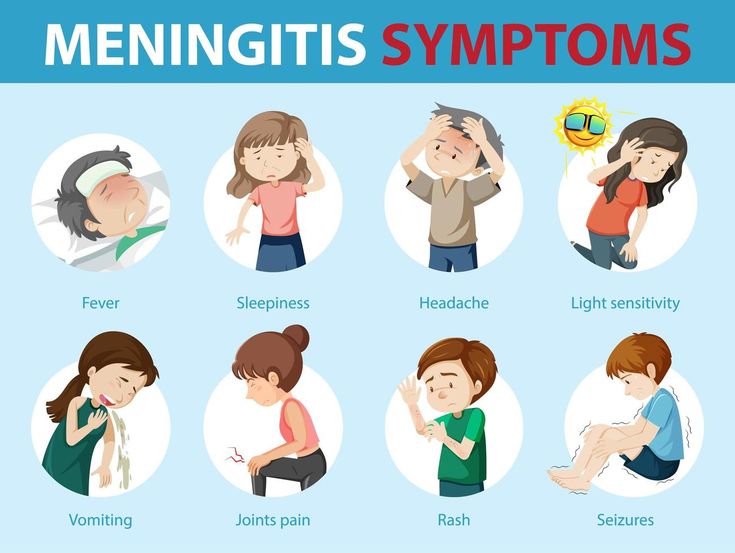
Symptoms of Bacterial Meningitis
Symptoms of bacterial meningitis appear fast, within hours or days. Early detection is important if treatment is to follow. Given below are some of the usual signs:
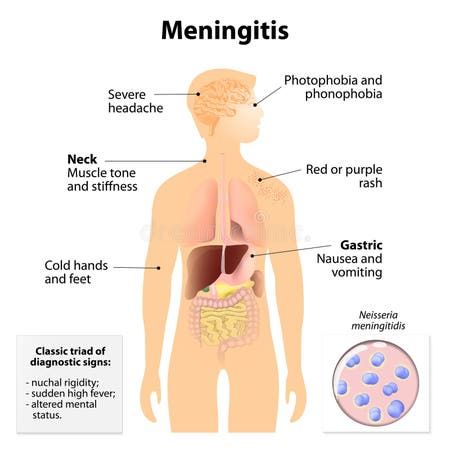
- Severe headache
- Neck stiffness
- High fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Photophobia
- Confusion and difficulty focusing
- Seizures
- Somnolence or inability fully to awaken
- Skin rash (choriomeningitis-meningococcal type)
Symptoms in newborns could be:
- Difficulty with feeding
- Constant crying
- Stiffness in the body
- Bulging fontanelle
- Low temperature
- Vomiting
-
How is bacterial meningitis diagnosed?
Bacterial meningitis is diagnosed through a combination of tests. The most common are:
Lumbar Puncture: A spinal tap that collects cerebrospinal fluid to analyze for infection.
Blood Tests: Blood samples are taken to check for bacteria in the bloodstream.
Imaging Tests: CT or MRI scans help identify inflammation or swelling in the brain.
Cultures: Culturing bacteria from blood or spinal fluid samples helps to pinpoint which species is involved.
PCR Tests: Tests to identify bacterial DNA in the cerebrospinal fluid in order to identify the bacteria quickly.
Management of Bacterial Meningitis
Everyone must treat it quickly or be denied it entirely with opposition to a disability over the whole course of life. Therefore, doctors prescribe antibiotics as symptoms appear until bacteria are eradicated. Common antibiotics used for treatment include penicillins, cephalosporins, and vancomycin.
They are the other treatments:
- Pain relievers for headaches and body pains
- Corticosteroids for decreased inflammation
- Intravenous fluids for dehydration prevention
- Oxygen therapy on very serious issues
Anticonvulsants
The choice of antibiotics will be determined by the organism causing the infection. Management has an increased chance of good outcome if the initiation of therapy is early.
For How Long is Treatment?
The duration of treatment may vary according to extent of infection. Antibiotics are usually given for about 7 to 21 days, and often hospitalization is mandatory, particularly in severe cases.
Complications of Bacterial Meningitis:
If untreated, bacterial meningitis can progress to severe complications such as:
- Damage in the brain
- Loss of hearing
- Seizures
- Memory problems
- Learning disabilities
- Loss of vision
- Kidney failure
- Shock
- Death (in severe cases)
Diagnosis and early treatment can significantly lower the chances of developing such complications, though some of them continue to produce long-term effects even after treatment.https://theechowriters.com/category/health-and-fitness/
Bacterial Meningitis Prevention
Indeed, it is better to prevent than to cure. Ways to help prevent bacterial meningitis include:
Vaccination: You can be vaccinated against some of the common bacteria, such as Hib, pneumococcus, and meningococcus.
Good Hygiene: One should wash their hands regularly and should avoid sharing personal effects, such as toothbrushes.
Healthy Lifestyle: Eating well and exercising regularly would also improve the immune system.
Avoid Close Contact: Sick people should be avoided.
Prenatal Care: Pregnant women should avoid eating contaminated foods and should get regular check-ups.
Vaccination is the best option to protect yourself and your loved ones from bacterial meningitis.
Risk factors for bacterial meningitis
Some factors could increase one’s risk of becoming infected with the bacteria that cause meningitis:
AGE: Young children and infants and elderly persons are at the highest risk.
IMMUNOCOMPROMISED: An immunocompromised host lacks adequate defence and hence increases the risk of potential infectious agents.
HEAD injuries: Any injury to the head should be treated since injury may also affect the underlying structures of the CNS or directly transmit agents of infections into the CNS.
LIVING IN CROWDED Places: Residential colleges, dormitories, and barracks have been documented as risk factors.
MISSED VACCINES:Any factor that may compromise these vaccinations, including an unvaccinated individual or failure to receive timely vaccinations.
CHRONIC DISEASES: Chronic diseases like diabetes or kidney disease can also increase susceptibility to bacterial infections.
Bacterial Meningitis vs. Viral Meningitis
Although many confuse bacterial meningitis and viral meningitis, they have major differences as shown in the table below:
| Bacterial Meningitis | Viral Meningitis |
| More severe | Less severe |
| Requires antibiotics | Often resolves without treatment |
| Can cause brain damage | Rarely causes complications |
| Contagious | Contagious |
| Higher mortality rate | Low mortality rate |
How to Help a Patient Suffering from Bacterial Meningitis?
Bacterial meningitis is a disease that requires proper and fast support during medical treatment to include loved ones in one’s life. Here are various suggestions on how to do that:
- Give emotional support
- Assist with daily activities
- Ensure they take drugs on time
- Encourage enough sleep and a balanced diet
- Hydrate well
- Follow the orders provided by the doctor.
Conclusion
Bacterial meningitis is a potentially fatal disease that is going to be treated in a hospital. However it is knowing the cause and symptoms as also preventive measures that will enable you and your family not to bit victim. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/11039-bacterial-meningitisVaccination and practicing good hygiene are vital as preventative measures, and any signs that could meet the criteria should therefore seek immediate medical treatment.
Saving lives through awareness about the disease can be achieved. Be well informed stay safe and stay healthy!