Chickenpox is a contagious disease that is brought about by the varicella-zoster virus. It occurs mostly in children but can also be experienced by adults. This blog gives elaborate information about chickenpox symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention. Follow along to understand how to keep yourself safe and effectively treat this illness.

What is chickenpox?
Chickenpox is a contagious illness that causes an itchy, red rash of spots and blisters. It easily spreads from person to person, particularly in children. Although it is typically mild, it can be serious in adults, pregnant women, and people with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms of Chickenpox
Its symptoms develop in stages and can include:
1. Early Symptoms
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Headache
2. Rash Development
- Small, red spots develop on the face, chest, and back.
- The rash develops on other parts of the body, including the scalp and mouth.
- Blisters filled with fluid develop over the spots.
- The blisters later burst and become scabs.
The whole process, from the appearance of the rash to the formation of scabs, takes around 7–10 days.
Causes of Chickenpox
It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is spread by:
- Direct contact with an infected person’s blisters.
- Airborne spread from coughs or sneezes.
- Contact with contaminated objects (e.g., clothing, bedding, or toys).
Who is at risk?
Anyone who has never had chickenpox or has not been vaccinated is at risk. However, some groups are more susceptible:
- Infants
- Pregnant women
- Individuals with compromised immune systems (e.g., cancer patients, organ transplant recipients)
-
How to Diagnose Chickenpox?
Physicians usually diagnose this disease on the basis of:
- Physical checkup of the rash
- Medical history of contact with an infected individual
- Blood work (in unusual cases)
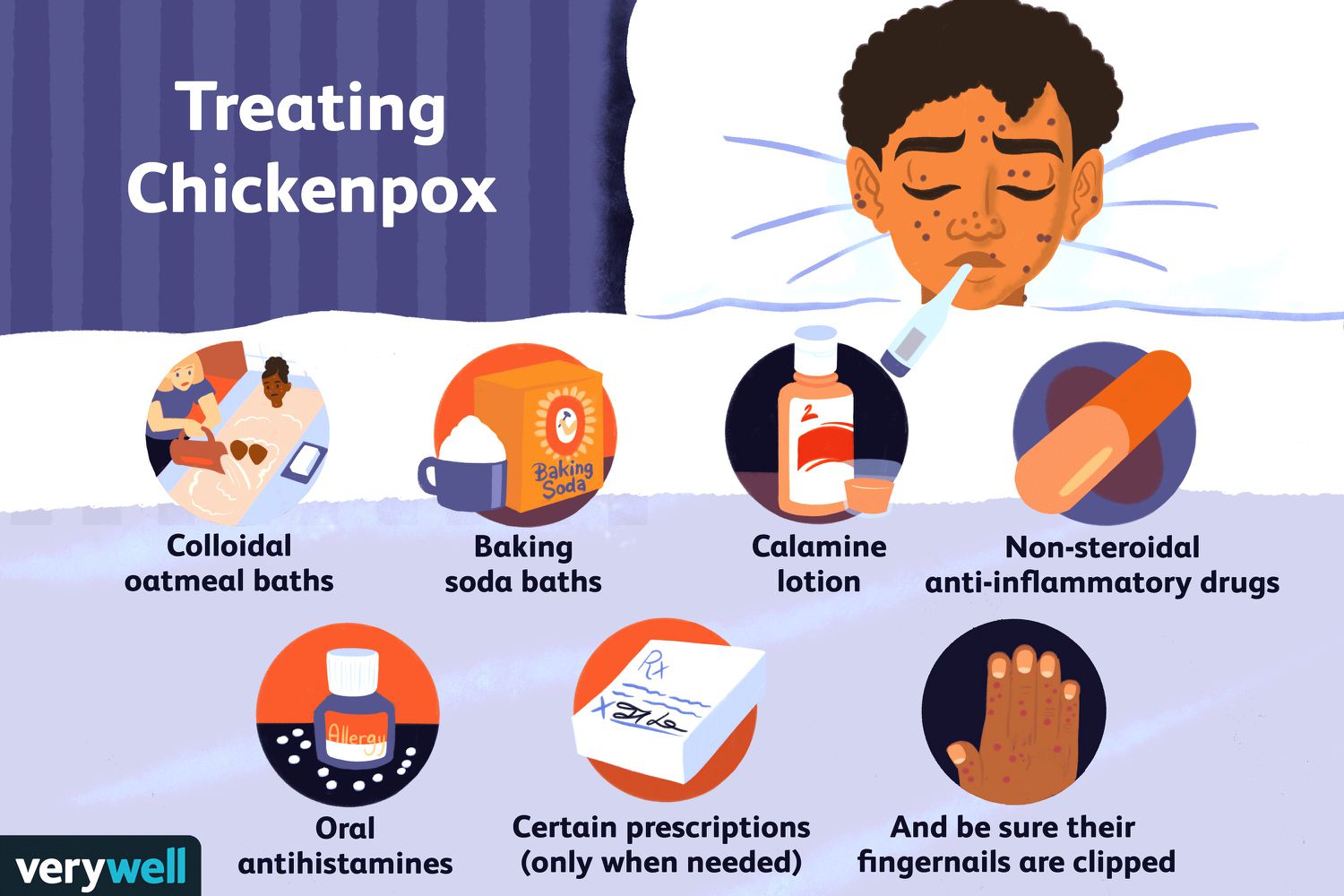
Chickenpox Treatment
There is no definite treatment for this disease, but symptoms are relieved and complications prevented.
1. Home Remedies
Rest and Fluids: Drink much fluid to keep yourself well-hydrated.
Cool Baths: Oatmeal baths help ease itching.
Calamine Lotion: Soothes the skin and eases itching.
Loose Clothing: Wear soft, loose clothing to avoid skin chafing.
2. Medications
Antihistamines: Keep the itch down and promote sleep.
Pain Relievers: Acetaminophen may also decrease fever and alleviate pain.
Antiviral Medications: Physicians prescribe antiviral medication to at-risk patients.
Complications of Chickenpox
Most cases of chickenpox are mild but may cause severe complications, including
- Skin infection due to over-scratching.
- Pneumonia in adults.
- Inflammation of the brain (encephalitis), although extremely rare.
- Birth defects in case a pregnant woman is infected.
How to Prevent?
1. Vaccination
Prevention of chickenpox is best achieved through vaccination. The varicella vaccine is
- Safe and effective against the disease.
- Recommended for kids, adolescents, and adults who have never had chickenpox.
2. Avoiding Contact with Infected People
- Avoid contact with chickenpox individuals until the blisters have scabbed over.
- If you are sick, remain home to avoid the transmission of the virus.
3. Proper Hygiene Practices
- Frequent handwashing with soap and water.
- Avoid touching eyes or face following contact with an infected individual.
- Clean surfaces and objects that are shared.
-
Chickenpox vs. Shingles: What’s the Difference?
Shingles is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox, which is the varicella-zoster virus. The virus lies dormant in the body after recovery from this disease and can recur later as shingles. Shingles results in a painful rash on one side of the body.https://theechowriters.com/category/health-and-fitness/
Conclusion
Chickenpox is a viral infection that is both common and can be prevented by vaccination and proper hygiene. Though most times it is not severe, in some people, it can result in complications. Knowing the symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention strategy can enable you to be protected and effectively deal with the disease.
By raising awareness, we can have improved protection against this disease and reduce its effect on people and communities.