Introduction
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition that results in widespread pain, fatigue, sleep disruptions, and cognitive dysfunction. Fibromyalgia mainly manifests in the muscles and soft tissues and tends to result in tender points in various parts of the body.
This is more prevalent in women than in men and may have a significant impact on daily functioning. Although research is ongoing, no one knows what causes fibromyalgia. It is, however, thought to involve an abnormal processing of pain in the brain.
In this blog, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatments, and prevention of fibromyalgia.

What is fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia is a chronic illness that induces widespread pain and tenderness in the body. It is defined as a neurological disorder since it influences the manner in which the brain and spinal cord interpret pain signals.
In contrast to arthritis, fibromyalgia neither induces inflammation nor joint damage, but it is capable of making the body extremely sensitive to pain.
Major Features of Fibromyalgia:
- Widespread pain for more than 3 months
- Tender points in certain areas of the body
- Fatigue and sleep disturbances
- Cognitive difficulties (fibro fog)
Causes of Fibromyalgia
The exact cause of this disease remains unknown. Still, researchers think that several factors are responsible for the condition.
Common Causes Include:
Abnormal pain processing: The nerves and brain overreact to pain messages.
Genetics: Fibromyalgia tends to run in the family.
Infections: Certain illnesses can trigger fibromyalgia.
Physical or emotional trauma: Traumatic events or injuries can trigger symptoms.
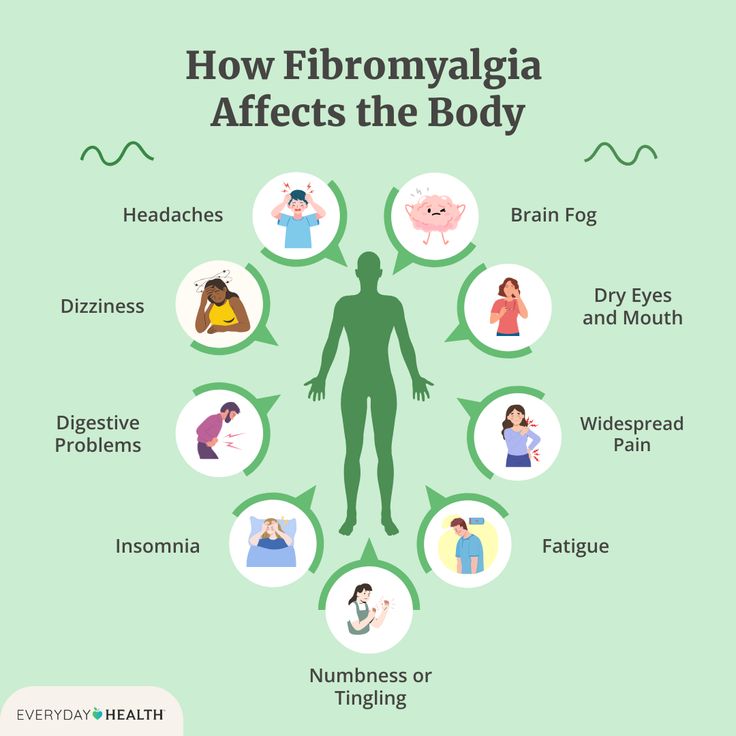
Symptoms of Fibromyalgia
Its symptoms differ from one individual to another and may vary over time. The most frequent symptom is widespread pain that persists for months.
Typical Symptoms Include:
- Chronic pain, stiffness, and tenderness in muscles
- Severe fatigue, even after resting
- Difficulty concentrating (“fibro fog”)
- Headaches and migraines
- Depression and anxiety
- Sleep disorders, including insomnia
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
-
Who is at risk?
Some factors make a person more likely to develop fibromyalgia.
High-Risk Individuals Include:
- Women (more susceptible to fibromyalgia than men)
- Individuals with a family history of fibromyalgia
- Patients with arthritis or other chronic pain disorders
- Those who have undergone physical or emotional trauma
- Patients with mood disorders such as anxiety or depression
How is it diagnosed?
There is no test for fibromyalgia, so physicians diagnose it on the basis of symptoms and medical history.
Diagnostic Methods Include:
- Physical examination to identify tender points
- Blood tests to exclude other conditions
- Screening for symptoms lasting ≥ 3 months
- Assessment of sleep and fatigue
Treatment for Fibromyalgia
It is not curable, but treatments are directed towards symptom control and enhancement of quality of life.
Medicinal Treatments:
- Pain medications (acetaminophen, ibuprofen)
- Antidepressants (to relieve pain and fatigue)
- Muscle relaxants
- Sleep aids
Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
- Exercise regularly (yoga, walking, swimming)
- Use relaxation methods (meditation, deep breathing)
- Eat a balanced diet (cut back on sugar and processed foods)
- Sleep well (establish a bedtime routine)
- Don’t use caffeine and alcohol
Diet and Nutrition
A healthy diet can decrease inflammation and increase energy levels.
Best Foods:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains (brown rice, oats, quinoa)
- Lean proteins such as fish and chicken
- Nuts and seeds (walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds)
Foods to Avoid:
- Processed foods and fast food
- Sugary snacks and beverages
- Too much caffeine and alcohol
- Artificial sweeteners and preservatives
Complications of Fibromyalgia
If untreated, it can greatly affect daily life.
Possible Complications Include:
- Severe exhaustion and low levels of energy
- Increased anxiety and stress
- Daily headaches or migraines
- Problem in maintaining work and social life
-
How to Prevent?
While it may not always be prevented, lifestyle modifications can sometimes lower the chances of developing the condition. https://theechowriters.com/category/health-and-fitness/
Prevention Tips:
- Regular exercise to maintain muscular strength
- Relaxation skills to control stress levels
- Having sufficient sleep to prevent exhaustion
- Balanced diet to ensure good health
Conclusion
It is a chronic and complicated disorder that influences millions of individuals across the globe. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4832-fibromyalgia Although it has no cure, with the right treatment, lifestyle modification, and stress management, one can lead a normal life.
If you have ongoing pain, tiredness, or difficulty concentrating, visit a physician for early detection and treatment.