Introduction
Anemia is defined as a common blood disorder in which the body does not possess enough healthy red blood cells to carry sufficient oxygen. Hence, fatigue, weakness, and other health complications arise. Anemia may be temporary or chronic, mild or severe, and any of its possible underlying causes.
This article discusses the details of anemia with respect to its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention tips. This understanding can help one take take necessary steps for maintaining good health.
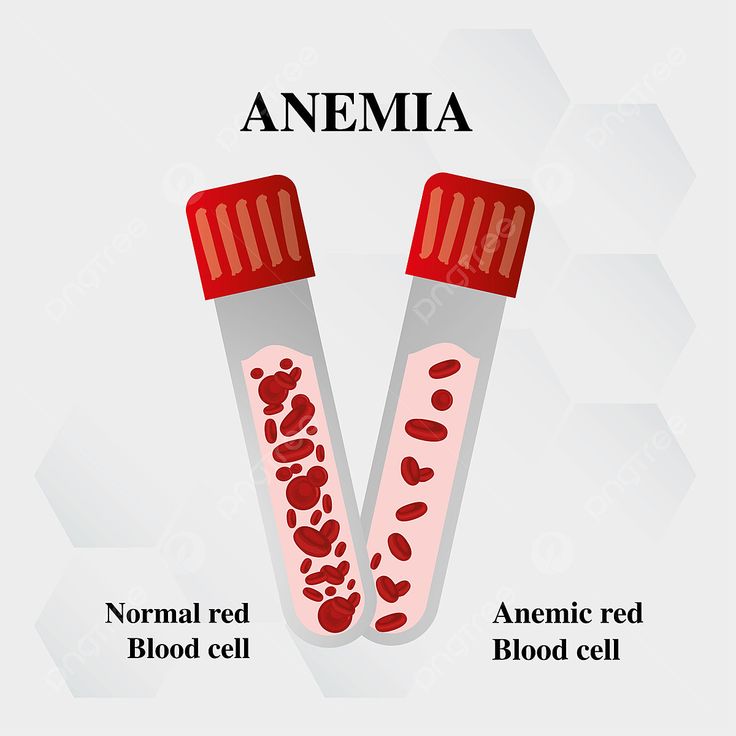
What is anemia?
Anemia is a health condition that occurs when the blood lacks enough healthy red blood cells and hemoglobin. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen from the lungs to different parts of the body.Low levels of hemoglobin mean that it is not enough in the body oxygen, leading to problems of different kinds.
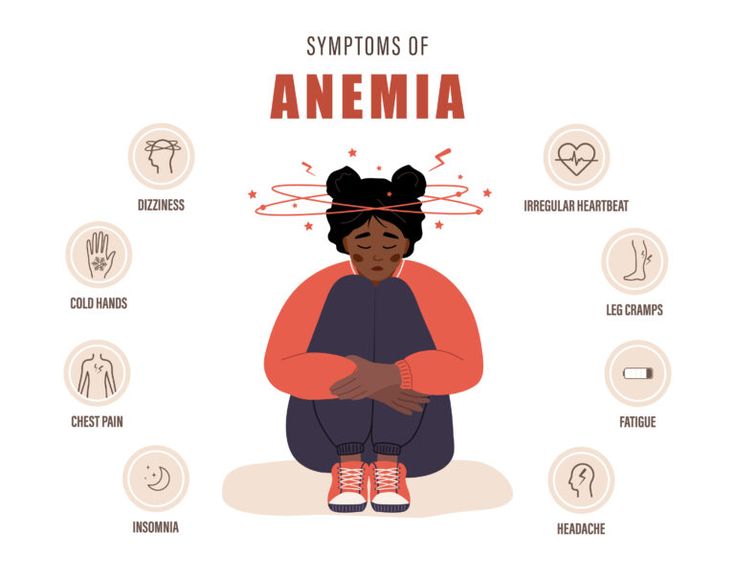
Symptoms of Anemia
The presentations will depend on the cause of this disease and its severity. The symptoms are as follows:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Cold hands and feet
- Irregular heartbeat
- Chest pain
- Headaches
Undetected anemia could lead to serious complications like heart problems and organ damage.
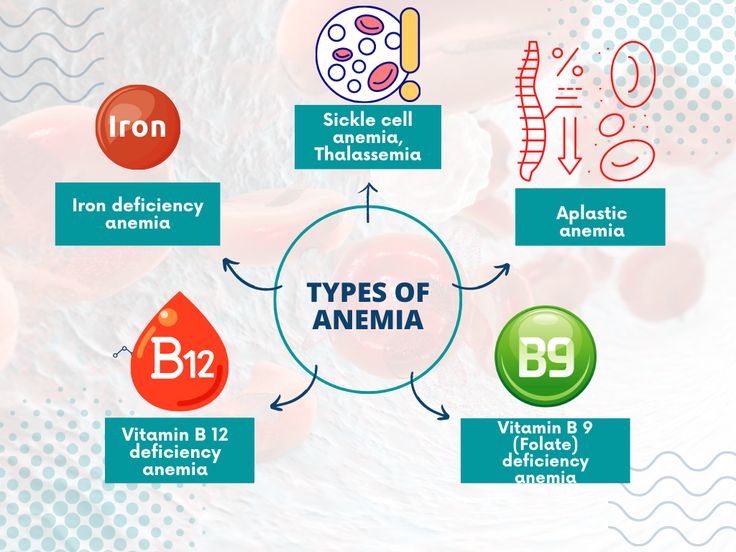
Causes of Anemia
It has different causes that could be nutritional, chronic disease related, or genetic. The main causes include:
1. Iron Deficiency Anemia
Iron is required in order to create hemoglobin. Failure in the availability of iron in the diet, blood loss, or absorption deficiency could finally result in iron deficiency anemia. Common causes include:
- Heavy menstrual periods
- Pregnancy
- Poor diets devoid of iron-rich foods
- Internal bleeding (ulcers, colon polyps, or cancers)
2. Vitamin Deficiency Anemia
The vitamins necessary for the body in the manufacture of red blood cells are vitamin B12 and folate. Deficiency in either of these vitamins can result in anemia. These may be caused by:
- Poor diet devoid of B12 or folate
- Malabsorption disorders (through conditions such as celiac disease or Crohn’s disease)
- Alcoholism
3. Aplastic Anemia
It’s a rare but serious condition in which the bone marrow produces too few red blood cells. It may be caused by:
- Autoimmune diseases
- Exposure to toxic chemicals
- Certain medications
- Viral infections
4. Hemolytic Anemia
This form of anemia occurs when an increased rate of destruction of red blood cells by the body exceeds the reformation of the cells by the bone marrow. Causes can include:
- Autoimmune diseases
- Infections
- Genetic disorders like sickle cell anemia.
5. Anemia of Chronic Diseases
Anemia that occurs as a secondary condition secondary to diseases, such as chronic kidney disease, cancer, or inflammatory diseases, may reduce the production of red blood cells.
6. Sickle Cell Anemia
An inherited kind of this disease in which red blood cells have a peculiar abnormal shape and there is decreased availability of oxygen to perfuse the organs, resulting in blood vessels obstruction.
How It Is Diagnosed?
The diagnostic tools utilized for this disease include:
Complete Blood Count: Checks hemoglobin level and red blood cell count.
Iron Studies: Determines iron levels in the body.
Vitamin B12 and Folate Tests: Evaluates vitamin deficiencies.
Bone Marrow Examination: Assesses bone marrow diseases.
Genetic Testing: Reveals inherited types of this disease.
Treatment Options
Management of this disease depends on its etiology. Some commonly used treatments are:
1. Iron Supplements and Diet
In iron deficiency anemia, an iron supplement is to be recommended along with dietary adjustments aimed at increasing the intake of iron-rich foods:
- Red meat, poultry, and fish
- Dark green leafy vegetables
- Beans and lentils
- Iron-fortified cereals
2. Vitamin Supplements
Treatment includes vitamin B12 or folic-acid supplementation or B12 injections.
3. Medications
In cases of chronic disease anemia, treatment of the underlying pathology may be instituted that sustains red blood cell production.
4. Blood Transfusions
In cases where this disease is very severe, blood transfusions may be necessary to rapidly restore levels of red blood cells.
5. Bone Marrow Transplant
In a plastic anemia or severe cases of sickle cell anemia, bone marrow transplantation becomes necessary.https://theechowriters.com/category/health-and-fitness/
Being Healthy Lifestyle is One Way of Prevent
It cannot be prevented in all of its forms, but a healthy lifestyle can effectively reduce the risk of becoming anemic. Here are the ways that can help:
Balanced diet: Along with the main food groups, also add sources of iron, vitamin B12, and folate-rich foods.
Taking supplements when necessary: Pregnant women and those with deficiencies will generally require supplements.
Avoid excessive alcohol consumption: Among other bad effects, alcohol also interferes with the absorption of nutrients.
Management of Chronic Conditions: Long-term diseases must follow respective advice from the doctor to avoid complications arising from them.
Regular health check-ups: It is only through early identification that this can be treated timely.
When to See a Doctor
Persistent fatigue, dizziness, or shortness of breath are enough reasons to see a doctor. Early diagnosis and initiation of treatment will prevent complications and improve the overall wellbeing.
Conclusion
One common but manageable condition is anemia. Educating themselves about causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this disease can help individuals proactively determine how they can manage their health.https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/3929-anemia Eating a healthy diet, adhering to a doctor’s recommendations, and seeking treatments in a timely manner can all help prevent complications that arise from it.
