Introduction
Arrhythmia is often described as the heart that beats irregularly. The heart may race or flutter slower or faster than it should. It affects everyone, irrespective of how old they are or what they do in life. However, knowledge about the disease, its causes, symptoms, and treatment can help detect its onset early and provide effective treatment management.
Through this blog, you will easily understand arrhythmia without jargon, which helps to make it sound clear to a large cross-section of readers. If you want to know the condition or help someone who may have it, this is a piece of information you will get.
What do you mean by arrhythmia?
Arrhythmia is an abnormal heart rate. The heart is responsible for pumping blood regularly and without stop. On occasions though, the heart develops an abnormal heart beat that can either be too fast (tachycardia), slow (bradycardia), or irregularly fast or slow.
Arrhythmia is sometimes asymptomatic; however, if left untreated, it can cause concern. For some arrhythmias, the proper treatment may be known; thus, an early reconnaissance of the specific arrhythmia is essential.
Detection of Arrhythmia and Assessment of its Implications
Arrhythmias are termed with respect to their echocardiographic origin and speed within the heart. The usual types include:
1. Tachycardia
Tachycardia, as the word suggests, is when the normal heart rate is exceeded, usually more than 100 beats per minute; it can occur in the different partitions of the heart, namely;
Atrial Tachycardia: There is a fast heart originating from the atria.
Ventricular Tachycardia: This quick rhythm is caused by the lower chambers of the heart.
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT): It is a fast rate originating above the ventricles.
2. Bradycardia
Bradycardia is a heart rhythm in which the heart beats slower than normal—this is usually less than sixty beats per minute. This can result in inadequate oxygen supply to the body organs.
3. Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
Atrial fibrillation is the condition where the top part of the heart, e.g., the atrium, is twitching and is fast and regular. However, it predisposes the individual to a risk of getting a stroke and heart failure.
4. Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation occurs when the heart suffers electrical chaos and the lower chambers of the heart do not beat in an organized manner to pump blood. This makes it a deadly emergency that requires immediate attention.
5. Premature Heartbeats
A heartbeat that occurs only partially in one heartbeat cycle, leaving the rest of the heartbeats to be completed later on. The result is that most chambers in the heart cannot experience the ove.
What Causes Arrhythmia?
Arrhythmias can result from different factors, such as:
Heart Disease: Coronary artery disease or heart attack
High Blood Pressure: Creates extra pressure on the heart
Electrolyte Imbalance: One has low concentration of potassium, calcium or magnesium
Stress and Anxiety: Such conditions may trigger a rapid heartbeat
Medicines: Several medicines may affect heartbeat.
Caffeine or Alcohol: Arrhythmia can be caused by overconsumption.
Genetic Factors: Whether anyone in the family possesses arrhythmias
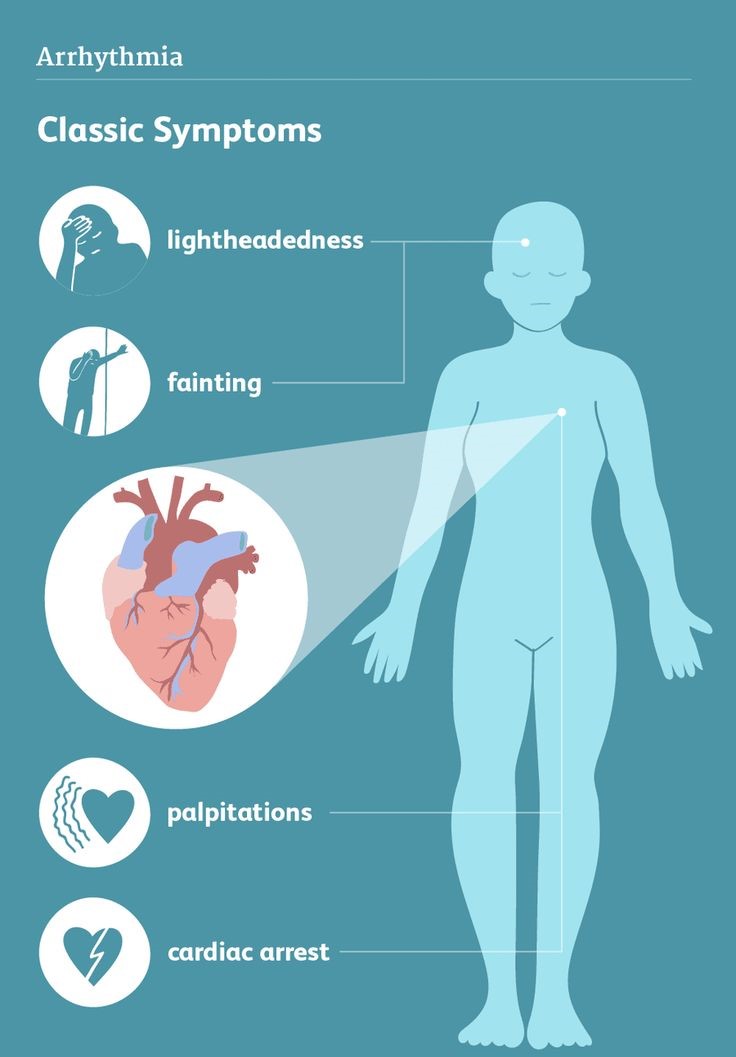
Symptoms of Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia can cause symptoms ranging from mild to severe. Commonly, symptoms include:
- Fluttering in the chest or palpitations
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Breathlessness
- Chest pain
- Loss of consciousness (syncope)
- Fatigue
- Sweating
If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a physician as soon as possible.
What methods are used to determine whether someone has an arrhythmia?
Various tests are commonly conducted to determine whether one has arrhythmia or not. Such tests may include the following:
Electrocardiogram (ECG): checkpoint cardiovascular method that records electrical operations of the upper chest. A permissible ECG chart is attached here; this provides a pictorial view as to what an ECG chart looks like.
Holter monitor: this is a telemetry with electrodes fixed on the chest for a period of 24 hours, 48 hours, or even a week to check every on the activity of the heart’s electricity, especially for the heartbeat irregularities. A nice Nybye is attached in pdf format.
Echocardiogram: this is generated by an echocardiogram, which produces pictures of the heart using sound waves; one can see the heart valves, heart walls, and blood vessels.
Stress test: a treadmill exercise test, which evaluates the function of the heart when exercising.
Electrophysiological study: Injection of medications and electronic mapping through radio frequency devices help pinpoint the area of the heart that needs to be ablated.https://theechowriters.com/category/health-and-fitness/
Treatment Options for Arrhythmia
The treatment principle in arrhythmia is determined on the basis of a particular occurrence regarding its type, causation, and severity. There are several therapeutic management options, such as.
1. Medicinal treatment
Doctors may provide drugs, for example, to slow down heartbeat, decrease the chances,atenolol, and also increase the rate of clots forming. Beta-blockers are some of the most common medications that include:
- cardio-selective drugs like atenolol which minimize side effects
- non-cardio selective like propranolol
- Calcium channel blockers
- Anti-arrhythmic drugs
2. Medical Procedures
Cardioversion: A use of controlled electrical shocks to stabilize the heart.
Catheter Ablation: this one removes the part of the heart tissue that is causing abnormal arrangment of heart contractions.
Pacemakers: these are wired devices fitted within a person’s chest to maintain a constant beating of the heart, particularly for individuals with very slow heart rates.
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD): is also an insertable device and helps in detecting and restoring harmful changes in the arrhythmias that are life-threatening.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Altering one’s living habits has a positive effect on avoiding arrhythmia. These include the following:
- Stopping the smoking habit
- Refraining from taking in so much caffeine and alcohol
- Engaging in exercise
- Dealing with stress and anxiety by using yoga and meditation techniques
- Eating food that will help to keep the heart in good condition.
Preventing Arrhythmia
Can Any Arrythmias be avoided, unaware of that with detailed suggestions?
The following tips will help you prevent the youngest arrythmias:
- Weight control is very important
- Monitor your blood pressure and cholesterol level
- Physical activity to be varied
- Keep away from too much coffee and alcohol
- Stress is hardly into you
- Go for heart check-ups occasionally
-
Symptoms of Risk
Several reasons increase the potential that arrhythmia will arise. The reasons are:
- Age (grow old)
- high blood pressure
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol
When to Call a Doctor
People should call a physician when they are:
- The occurrence of chest pain at lightening-like continuity.
- They have difficulty breathing and feel as though they are fainting.
- The sensation of dizziness or severe giddiness is intense enough.
- They had a series of insufficient heartbeats for many minutes.
Conclusion
Arrhythmia is a prevalent condition of the heart that may need immediate attention if encountered and is chaotically a health challenge that could sprout. By both looking for the cause symptoms and possible treatments, this health issue can be solved.https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16749-arrhythmia In such cases, when steps are taken by the patient to clear the stresses that might be contributing to the arrhythmias, the condition goes all of a sudden. Your health is your responsibility; hence, do not wait for the doctor’s command; take care of your heart.
If you enjoyed this read, feel free to help others access this useful information by sharing it with them. After all, prevention is better than cure.
