Introduction
The bacteria of the Brucella genus cause brucellosis, an infectious disease. It primarily affects animals like cattle, goats, sheep, and pigs but can spread to humans through direct contact with infected animals or by consuming contaminated animal products. If left untreated, the disease can lead to severe health complications.
Here, we will extensively talk about brucellosis: the causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, and prevention. If you have a basic knowledge of coding, consider brucellosis to be a system vulnerability—once the bacteria find their way into the human body, they disrupt normal functions, just like malware may slow down a program.
What is Brucellosis?
Brucellosis is a bacterial zoonosis.People may refer to it as Malta fever, Mediterranean fever, or undulant fever.This disease has the potential to attack multiple organ systems and, if not treated in due time, can lead to chronic illness.
How Brucellosis Spreads.
Brucellosis spreads via several pathways:
Direct Contact: Handling infected animals or their secretions without protection or without the use of protective equipment.
Ingesting Food Stuff: drinking unpasteurized milk or eating dairy products from infected animals.
Inhaling bacteria: Farmers, vets, and slaughterhouse workers are at risk when airborne.
Mother-to-Child Transmission: In occasional cases, it may be transmitted while breastfeeding or during childbirth.
Causes of Brucellosis
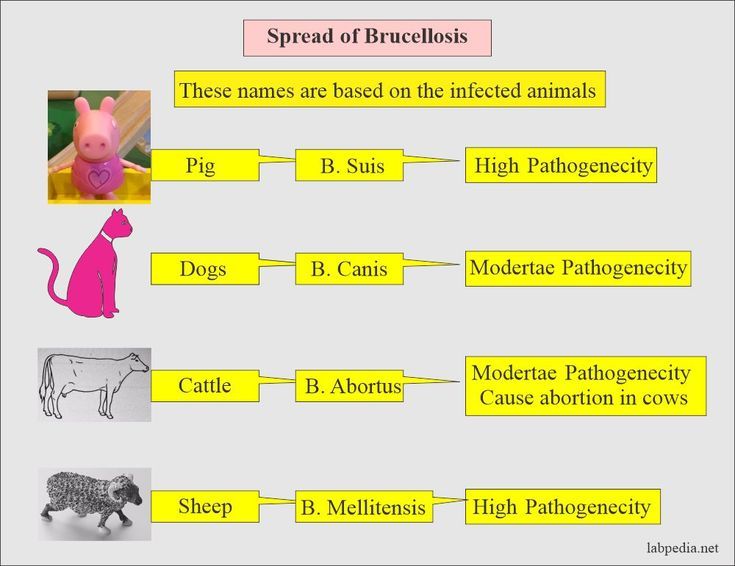
Different species of Brucella cause brucellosis. Brucella melitensis, the most prevalent in humans, infects goats and sheep.
- Cattle carry Brucella abortus, which causes bovine brucellosis.
- Brucella suis infects pigs and can cause intense infections in humans.
- Brucella canis affects dogs, but documented human cases are rare
Brucella infects lymph organs after gaining entry through mucous membranes, cuts, or ingestion and then travels via the lymphatic system to infect various organs. https://theechowriters.com/category/health-and-fitness/
Symptoms of Brucellosis
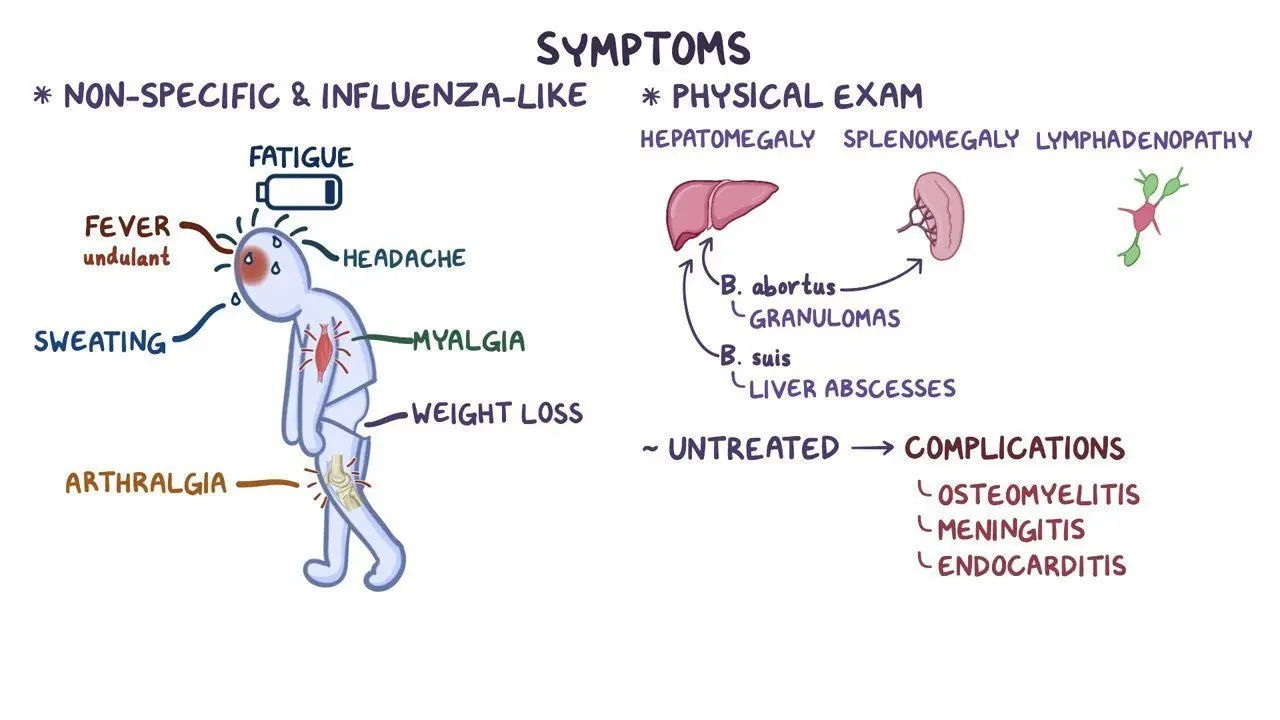
Brucellosis ranges from very mild to so severe that it can mimic a flu-like illness, and it can take place between a few days and several months after exposure to the infectious agent.
The most common symptoms include:
- Fever, often rising and falling (known as undulant fever)
- Excessive sweating, usually at night.
- General malaise and weakness.
- Body aches or joint pain.
- Headaches.
- Loss of appetite.
- Weight Loss.
Severe Symptoms:
- Arthritis and joint pains.
- Enlarged liver and spleen.
- Neurological symptoms such as depression and confusion.
- Endocarditis (which is fatal) depicts infection of the lining of the heart.
Brucellosis without treatment quickly becomes chronic. Subsequently, it may lead to the development of chronic illness.
Brucellosis diagnosis
The diagnosis of brucellosis is often complicated since it manifests a symptomology similar to many other diseases. However, a doctor uses the following methods to diagnose brucellosis:
Blood tests: to detect antibodies or bacterium in blood.
Bone Marrow Culture: More precise but infrequently used since it is invasive.
Serological tests: detect relative antibody profiles by Brucella.
Imaging Tests: CT scan or MRI for detecting complications in any of the organs or joints.
Treatment of Brucellosis
Brucellosis requires long-term treatment with antibiotics to prevent relapse. Antibiotic treatment is mostly done using the following drugs:
Doxycycline: to be taken for at least six weeks.
Rifampin: given with doxycycline in order to improve efficacy.
Streptomycin or Gentamicin: given in severe cases.
Most patients recover with treatment; however, a portion may recover with some symptoms that require prolonged therapy.
Complications of Brucellosis
If untreated, the brucellosis may lead to serious complications, including:
- Chronic pains in joints and arthritis
- Endocarditis: inflammation in the heart
- Severe neurological disorders
- Liver abscesses
Early detection and treatment can prevent these complications.
Prevention of Brucellosis
Prevention of brucellosis is reduction of exposure to the bacterium. Following are some of the proven means of effective prevention:
Avoid Unpasteurized Dairy: Eat only pasteurized milk and dairy products.
Wear protective equipment: Farmers and veterinarians should put on gloves and even preferably masks while handling animals.
Good personal hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly after handling animals or raw meat.
Vaccinate Animals: Vaccinating livestock tends to decrease the possibility of transmission.
Cook Meat Properly: Ensure meat is cooked to safe temperatures before consumption.
Brucellosis in Different Regions
Brucellosis is confined to certain areas in the world, especially where unpasteurized products are widely eaten. High-risk areas for infection with brucellosis include:
- Middle Eastern countries
- Countries in South and Central America
- Africa
- Countries in Asia
- Countries along the Mediterranean
Travelers in these areas should take some precautions to avoid infection with the disease.
Brucellosis Compared with Other Bacterial Infections
| Feature | Brucellosis | Tuberculosis | Lyme Disease |
| Cause | Brucella bacteria | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Borrelia burgdorferi |
| Transmission | Animal contact, food | Airborne | Tick bites |
| Symptoms | Fever, joint pain, fatigue | Cough, weight loss, fever | Rash, joint pain, flu-like symptoms |
| Treatment | Antibiotics (Doxycycline + Rifampin) | Antibiotics (Isoniazid, Rifampin) | Antibiotics (Doxycycline) |
Living With Brucellosis
Living with chronic brucellosis can affect one’s normal life. Patients are advised to:
- Follow their physician’s recommendations.
- Take healthful foods with exercise.
- Schedule check-ups to follow up on symptoms.
- Seek mental health care for treatment of depression and anxiety.
Conclusion
Brucellosis is one of the serious bacteriological infections that spread from animals to people. It gives flu-like symptoms and, if untreated, leads to greatly severe complications. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17886-brucellosisThe keys to preventing and controlling the disease are early diagnosis, proper antibiotic treatment, and prevention.
Awareness about brucellosis and taking all precautions are ways through which we can now avoid and minimize the impacts, thus protecting human and animal health from this disease.