Introduction
Chanarin disease, or Neutral Lipid Storage Disease with Ichthyosis (NLSDI), is a rare hereditary disorder of fat metabolism in the body. It occurs due to mutations in the ABHD5 gene, with the resultant accumulation of fats (lipids) in the tissues. Its most evident symptom is ichthyosis, which is a skin disorder manifesting itself as scaly dry skin. Along with skin issues, Chanarin disease may extend to the liver, muscles, and other organs, causing complications in the long run.
Knowing Chanarin disease can help in early diagnosis and improved management. In this blog, we’ll be learning the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of this unusual disorder. If you know basic coding, imagine Chanarin disease as a “bug” in the body’s fat storage system that creates errors which interfere with normal functioning, similar to how a defective program would impact a computer.

What Causes Chanarin Disease?
Chanarin disease is an autosomal recessive inherited condition, and a person needs to inherit a defective gene from both parents to develop the condition. The main cause is a mutation in the ABHD5 gene, which is responsible for the breakdown of lipids in the body. When this gene fails to work, fats get stored in various organs, causing symptoms.
How is Chanarin Disease Inherited?
If both parents are carrying a defective gene, the child has a 25% chance of getting the disease.
- If only one gene is inherited, a child has a 50% chance of being a carrier (asymptomatic).
- There is a 25% chance that the child may not inherit the defective gene whatsoever.
This disorder occurs more frequently in consanguineous (closely related) marriages as the likelihood of inheriting two defective genes is greater.
Chanarin Disease Symptoms
Chanarin disease symptoms manifest at birth or infancy and aggravate over time. The most prevalent symptoms are:
Skin Symptoms
- Ichthyosis: Scaly, dry skin that looks like fish scales.
- Red or erythematous patches of skin.
- Thickened palm and sole skin.
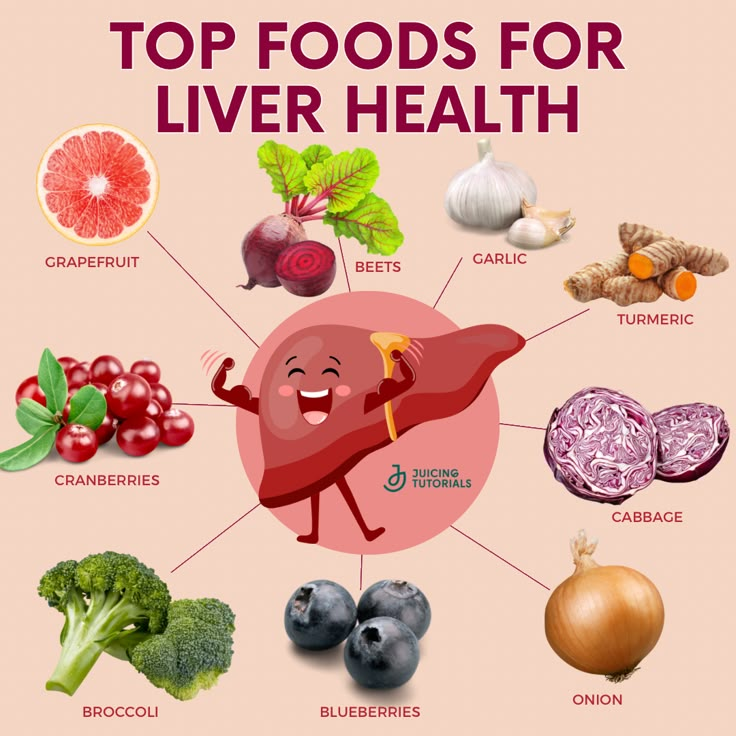
Liver and Digestive Symptoms
- Hepatomegaly: Enlarged liver due to fat deposition.
- Fatty liver disease, which can cause liver damage.
- Malabsorption of nutrients and growth retardation.
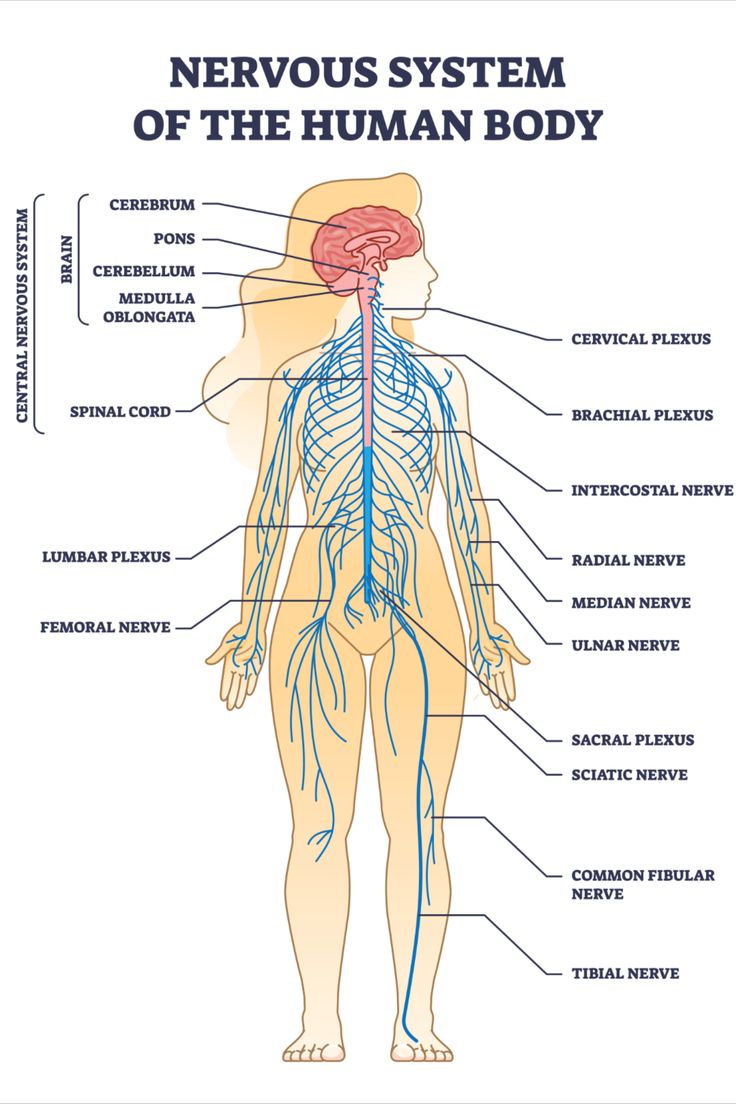
Muscle and Nervous System Signs
- Muscle fatigue and weakness.
- Delayed child motor development.
- Impaired hearing and vision in a few instances.
- Neurological problems like seizures (in very infrequent instances).
-
Other Signs
- Enlarged spleen in a few patients.
- Abnormal blood, including elevated levels of lipid-laden white blood cells (Jordans’ anomaly).
- Late speech and mental development in exceptional instances.
Diagnosing Chanarin Disease
Precise diagnosis of Chanarin disease can facilitate enhanced management of the symptoms. Some tests are conducted by physicians for the confirmation of this condition:
Physical Examination: Physicians check dryness of skin, scaly lesions, and other outward features.
Blood Tests: Lipid-laden white blood cells (Jordans’ anomaly) may be apparent in a blood smear.
Genetic Testing: DNA testing affirms mutations of the ABHD5 gene.
Liver Biopsy: In suspected liver involvement, a biopsy indicates fat deposition.
Muscle Tests: Electromyography (EMG) can be done to test muscle function.
Treatment for Chanarin Disease
This disease is not yet curable, but treatment involves the management of symptoms and enhancement of quality of life.
1. Skincare Management
- Topical moisturizing creams and lotions decrease skin dryness and scaling.
- Keratolytic agents (salicylic acid or urea creams) soften thickened skin.
- Vitamin A supplements (with physician monitoring) might improve ichthyosis.
2. Dietary Changes
- Low-fat diet to prevent lipid buildup in the liver.
- Protein-rich foods to promote muscle strength.
- Omega-3 fatty acids (from fish oil) for anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Prevention of alcohol consumption to avoid liver complications.
3. Liver and Muscle Management
- Routine tests of liver function to track advancement.
- Physiotherapy and exercise to promote muscle strength and avoid atrophy.
- Neurological support in case of cognitive or motor delay.
-
4. Regular Monitoring
- Eye and hearing tests to identify complications early on.
- Tracking of growth and development in children.
- Specialist consultations (dermatologists, hepatologists, neurologists) for long-term care.
Prevention of Chanarin Disease
As Chanarin disease is a genetic disorder, prevention is largely in the form of genetic counseling and awareness.
Genetic Testing: Individuals who have a history of the disease in their families can be genetically screened prior to conception.
Carrier Testing: The parents can be tested to see if they are carriers.
Prenatal Diagnosis: Pregnant women can also undergo genetic testing to see if the fetus is carrying the mutation.
Consanguineous Marriage Awareness: Informing consanguineous communities about marrying close relatives risks.https://theechowriters.com/category/health-and-fitness/
Chanarin Disease vs. Other Lipid Storage Disorders
Chanarin disease is just one of many lipid storage diseases. Here’s how similar disorders are compared:
| Feature | Chanarin Disease | Gaucher Disease | Fabry Disease |
| Cause | ABHD5 Gene Mutation | GBA Gene Mutation | GLA Gene Mutation |
| Symptoms | Ichthyosis, liver problems, muscle weakness | Enlarged liver, bone pain, anemia | Skin rash, pain, kidney issues |
| Inheritance | Autosomal recessive | Autosomal recessive | X-linked recessive |
| Treatment | Supportive care | Enzyme replacement therapy | Enzyme replacement therapy |
Living with Chanarin Disease
While living with this disease might be difficult, appropriate medical management and lifestyle change can enhance a patient’s way of life. Individuals with the disorder should:
- Adhere to a skincare schedule to avoid abnormal dryness.
- Eat a healthy diet to avoid liver and muscular complications.
- Adopt regular exercises to build strong muscles.
- Seek regular checkups to track the progress and avert complications.
Participate in support groups to interact with others experiencing comparable challenges.
Conclusion
Chanarin disease is a rare but serious inherited lipid metabolism disorder that causes skin, liver, and muscle involvement. Although no cure exists, early diagnosis and appropriate management significantly enhance the quality of life for a patient.https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/chanarin-dorfman-syndrome/ Familiarity with the signs, genetic counseling, and necessary lifestyle modifications allow affected individuals and their families to live healthier.
By increasing awareness and encouraging research, we can enhance the diagnosis and treatment of rare genetic conditions such as Chanarin disease.