Introduction
Cirrhosis Disease is a chronic liver illness that develops when normal liver tissue is replaced by fibrosis, or scar tissue, over time. This scarring disrupts the normal functioning of the liver and causes serious health problems. The liver performs essential functions of detoxification, metabolism, and digestion, and thus its health is vital for the body as a whole. It is important to know the causes, symptoms, and treatment of cirrhosis in order to effectively manage and prevent this condition.

What is Cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis is a late liver disease that involves fibrosis (scarring) of the liver. As healthy liver cells are replaced by scar tissue, the liver’s functioning capacity decreases. This can, over time, result in liver failure, a potentially fatal condition. Although cirrhosis cannot be reversed completely, early detection and appropriate treatment can halt its progression and enhance the quality of life of the patient.
Causes of Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis may develop from many long-term liver illnesses and diseases. Among the most prevalent causes are:
Chronic Drinking: Overuse of alcohol over a prolonged period destroys liver cells, and as a result, causes scarring.
Infections of Hepatitis B and C: The viral infections produce inflammation and liver damage, with the potential of cirrhosis.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): A condition in which fat accumulates in the liver, commonly associated with obesity and diabetes.
Autoimmune Hepatitis: An illness in which the immune system incorrectly targets liver cells, leading to inflammation and fibrosis.
Genetic Liver Diseases: Illnesses such as Wilson’s disease and hemochromatosis result in excess deposition of metals in the liver, leading to damage.
Biliary Diseases: Primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis are conditions that block bile ducts, resulting in liver damage.
Toxins and Medications: Chronic exposure to toxic chemicals and some medications can lead to scarring of the liver.
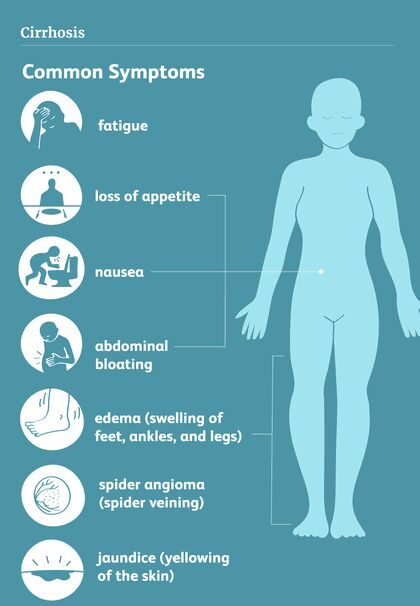
Symptoms of Cirrhosis
In the initial stages, cirrhosis might not produce any symptoms. As the disease advances, the following symptoms may develop:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and abdomen (ascites)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Itchy skin
- Dark urine and pale stools
- Confusion or trouble concentrating (hepatic encephalopathy)
- More tendency to bruise or bleed easily
- Spider-like blood vessels on the skin
-
How Is Cirrhosis Diagnosed?
Physicians diagnose Cirrhosis Disease with a combination of history taking, physical examination, and the use of tests, such as:
Blood Tests: To assess liver enzyme levels and liver function overall.
Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans allow for the detection of scarring in the liver and structural changes.
Liver Biopsy: A small sample of tissue is looked at microscopically to verify cirrhosis and determine severity.
Endoscopy: To look for enlarged veins (varices) in the digestive tract caused by liver damage.
Treatment of Cirrhosis
Although cirrhosis can’t be cured, treatment is aimed at reducing symptoms and preventing additional liver damage.
1. Lifestyle Changes
Stay Away from Alcohol: Stopping alcohol consumption altogether is necessary to avoid further liver damage.
Healthy Diet: Following a balanced diet with lots of fruits, vegetables, and lean protein supports the functioning of the liver.
Exercise Regularly: Regular exercise aids in obesity management and minimizes fat storage in the liver.
2. Medications
- Antiviral medications for hepatitis B and C infections.
- Medications to decrease liver inflammation and decelerate fibrosis.
- Diuretics to decrease fluid buildup in the abdomen and legs.
- Laxatives such as lactulose to aid in the excretion of toxins from the body in hepatic encephalopathy.
3. Medical Procedures
Paracentesis: A surgical intervention to remove excess fluid from the abdomen in severe ascites.
Endoscopic Therapy: To cure bleeding varices in the digestive system.
Liver Transplant: In extreme cases, a liver transplant is the only hope for survival.
Home Remedies for Managing Cirrhosis
Along with medical treatments, home remedies and lifestyle modifications can help control cirrhosis symptoms:
- Drink as much water as possible to maintain hydration.
- Limit salt intake in order to restrict fluid buildup.
- Skip processed foods and fatty meals.
- Take herbal supplements such as milk thistle (use after consulting a physician).
Complications of Cirrhosis
Untreated, cirrhosis can result in serious complications, including:
Liver Failure: When the liver ceases to function at all.
Portal Hypertension: Raised pressure in the portal vein resulting in distended veins and bleeding.
Hepatic Encephalopathy: Accumulation of toxins in the brain leading to confusion and coma.
Liver Cancer: Cirrhosis raises the risk of liver cancer.
Kidney Dysfunction: Also referred to as hepatorenal syndrome, impacting kidney function.

Prevention of Cirrhosis
Prevention of cirrhosis entails guarding the liver against damage. Some of the important preventive actions include:
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Avoid excessive alcohol consumption to decrease liver stress.
Get Vaccinated: Hepatitis B vaccines can prevent liver infection.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity reduction decreases the risk of fatty liver disease.
Practice Safe Hygiene: Do not share needles or personal items that can transmit hepatitis.
Eat a Nutritious Diet: Fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats in the diet promote liver health.
Is Cirrhosis Reversible?
Cirrhosis in its initial stages can be treated with lifestyle modification and medication, but advanced cirrhosis is irreversible. The most important thing is early detection and management to retard progression and enhance life expectancy. https://theechowriters.com/category/health-and-fitness/
Conclusion
Cirrhosis Disease is a serious illness that affects the liver and needs to be treated at an early stage along with proper care. Though the condition cannot always be reversed, changes in lifestyle, medical treatment, and preventive care can enhance the function of the liver and overall health. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15572-cirrhosis-of-the-liver If you notice any symptoms of cirrhosis, immediately consult a medical practitioner for proper diagnosis and cure.