Introduction
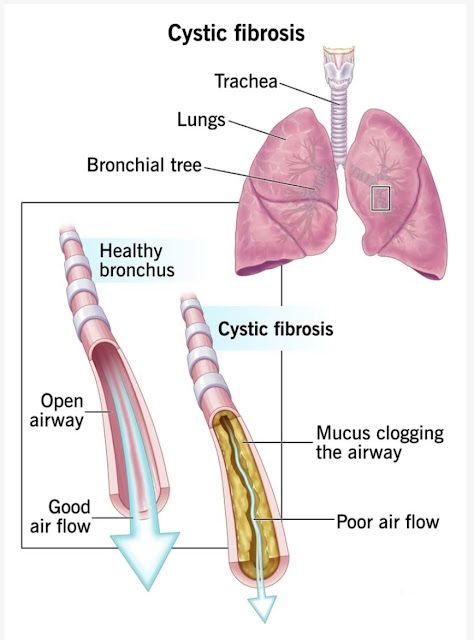
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disease that occurs in the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive tracts. CF causes the release of thick, sticky mucus that blocks the airways and results in chronic lung infections. The condition is also inherited and affects the pancreas, liver, and other organs, hindering the body from absorbing nutrients effectively. Untreated CF may result in fatal complications.
In this blog, we are going to deconstruct all you need to know about cystic fibrosis. If you know basic coding, consider CF a programming glitch that interferes with normal system operation. Just as a glitch in a program may result in many problems, a genetic defect in CF results in widespread illness.
What is cystic fibrosis?
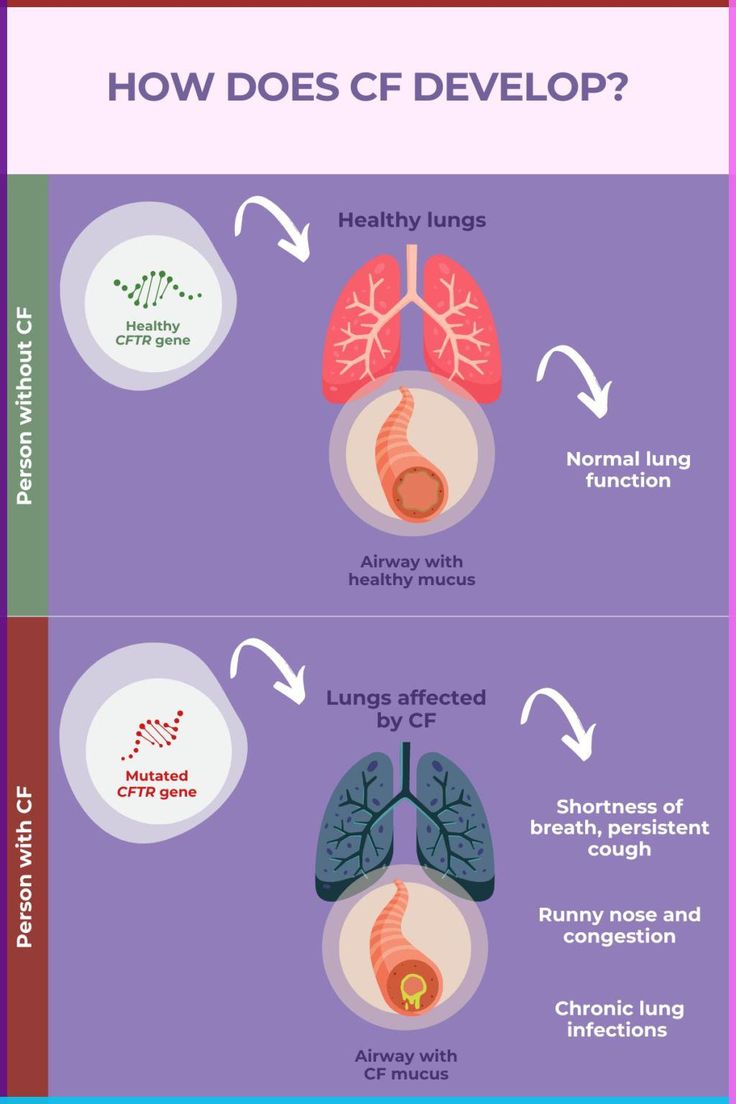
Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease due to mutations in the CFTR (Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator) gene. The CFTR gene controls the flow of salt and water in and out of cells. When the CFTR gene is faulty, the body makes thick mucus, which accumulates in various organs, particularly the lungs and intestines.
How is Cystic Fibrosis Inherited?
CF is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder, so a child must receive two defective CFTR genes (one from each parent) to get the disease. If someone inherits a single defective gene, they are a carrier but do not have symptoms.
Causes of Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is the result of a mutation in the CFTR gene. The mutation is responsible for improper chloride ion transport, and there is defective chloride ion production and thick mucus production. The CFTR gene has more than 2,000 known mutations, but ΔF508 is the most common.
Factors that affect CF severity:
- Type of CFTR gene mutation
- Environmental factors
- Accessibility to medical attention
- Diet and lifestyle
Symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis
Symptoms of CF range from mild to severe and involve several organs. The disease is usually apparent in infancy or early childhood, but a few are diagnosed later.
Respiratory Symptoms:
- Chronic cough with thick mucus
- Recurrent lung infections (pneumonia, bronchitis)
- Shortness of breath and wheezing
- Stuffy nose and sinus infections
Digestive Symptoms:
- Poor weight gain and growth
- Greasy, foul-smelling stools
- Intestinal blockage (meconium ileus in newborns)
- Severe constipation
Other Symptoms:
- Clubbing of fingers and toes (due to low oxygen levels)
- Male infertility (due to clogged vas deferens)
- Skin with a salty taste (owing to excessive loss of salt through sweat)
-
Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis
Improved life expectancy and quality of life are achieved with early diagnosis. The following diagnostic tests identify CF:
Newborn Screening—It is a blood test that examines for elevated concentrations of immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT), signifying CF.
Sweat TestChecks the concentration of salt in the sweat, since individuals with CF have increased amounts of chloride.
Genetic TTestingiscovers CFTR mutations in presumptive cases.
Lung Function TeTests Tests how well the lungs function.
Chest X-rays & CT Scans— Find lung damage and mucus accumulation.
Treatment and Management of Cystic Fibrosis
There is no cure for CF, but it is treated to manage symptoms, avoid complications, and enhance quality of life.
Medications
Mucus-Thinning MedicationsBreak up thick mucus in airways (e.g., Dornase Alfa).
Bronchodilators —dilateairways and facilitate breathing.
Antibiotics—Eradicate lung infections.
CFTR ModulatorsEnhance the defective CFTR protein function (e.g., Ivacaftor, Lumacaftor).
Digestive EEnzymesacilitate nutrient absorption by breaking food down.
Airway Clearance Therapies
Chest physiotherapy –—loosenLoosens mucus in the lungs.
Oscillating—shakests – Shakes the chest to disperse mucus.
Posturdrainage—e – Utilizes gravity to drain mucus from airways.
Lifestyle and Home Treatments
Nutrient-Rich Diet—High-protein, high-calorie food.
Frequent Hydration—Avoids dehydration and mucus thickness.
Regular Exercise—Maintains lung performance.
Avoiding Germs—Decreases chances of infections.
Surgical Therapies
In extreme cases, lung transplantation is a possibility for patients with advanced lung disease.
Complications of Cystic Fibrosis
CF can result in severe health complications if not treated well. Some of these are:
Respiratory failure—becausebecause of frequent lung infections.
Diabetes—CF-related diabetes (CFRD) impairs glucose regulation.
Osteoporosis – Weakened bones due to impaired calcium absorption.
Liver Disease—Obstruction of bile ducts leads to liver damage.
Infertility—9898% of men with CF are unable to conceive because the reproductive ducts are obstructed.
Prevention of Cystic Fibrosis
CF,, being a genetic condition,, cannot be prevented. However, genetic counseling can make the individuals aware of the chances of their child having CF. Carrier screening is possible prior to conception so that they may know their possibility of having a child with CF.
Living with Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is a condition that needs to be managed throughout one’s life, but with today’s medicine, people with CF are living longer and healthier. Support groups, frequent checkups, and mental health care can make a big difference in overall health.
Tips for Coping with CF on a Daily Basis:
- Take medication and therapy as prescribed.
- Eat a healthy diet and drink plenty of water.
- Exercise regularly.
- Stay away from smoke and pollutants.
- Stay informed about CF research and emerging treatments.
Cystic Fibrosis vs Other Respiratory Diseases
| Feature | Cystic Fibrosis | Asthma | COPD |
| Cause | Genetic mutation | Allergies, inflammation | Smoking, pollution |
| Symptoms | Thick mucus, infections | Wheezing, breathlessness | Chronic cough, mucus buildup |
| Treatment | Medications, physiotherapy | Inhalers, steroids | Oxygen therapy, bronchodilators |
| Prevention | Genetic testing | Avoid triggers | Quit smoking |
Future of Cystic Fibrosis Treatment
CF treatment is getting better with ongoing medical research. Researchers are working on gene therapy, mRNA-based medications, and CRISPR gene editing to repair the CFTR mutation at the genetic level. These developments provide promise for a future cure. https://theechowriters.com/category/health-and-fitness/
Conclusion
Cystic fibrosis is a serious but manageable genetic disorder. Learning about its causes, symptoms, and treatment can enable individuals to live healthier lives. Though CF is still not curable, medical science has made it possible to substantially enhance the quality of life in CF patients. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9358-cystic-fibrosisThrough awareness creation and continued research, we can bring ourselves closer to improved treatment and, in time, a cure.
If you or the person you know has CF, being well-educated and proactive may be a matter of huge influence. Always go to healthcare practitioners for individual recommendations and treatment regimes.