Introduction
Diabetes is one of the most prevalent chronic health conditions worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. Understanding diabetes, its causes, symptoms, and management strategies is essential to maintaining good health. In this blog, we’ll dive into the essentials of diabetes, providing useful insights for those seeking to better understand this condition.

What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a health condition in which the body is unable to produce sufficient insulin or is unable to utilize the insulin it does produce. Insulin is a hormone that assists in maintaining blood sugar levels. There are two primary forms of diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune disease in which the body attacks the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin.
Type 2 Diabetes: A more prevalent type in which the body does not use insulin properly or is unable to make enough insulin.
Gestational diabetes is a temporary type that occurs during pregnancy.
The Need to Manage Diabetes
Diabetes management is important for living a healthy life. When this disease is left unchecked or inadequately managed, it can result in life-threatening complications like heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage. With proper treatment, individuals with this disease can live active and healthy lives.
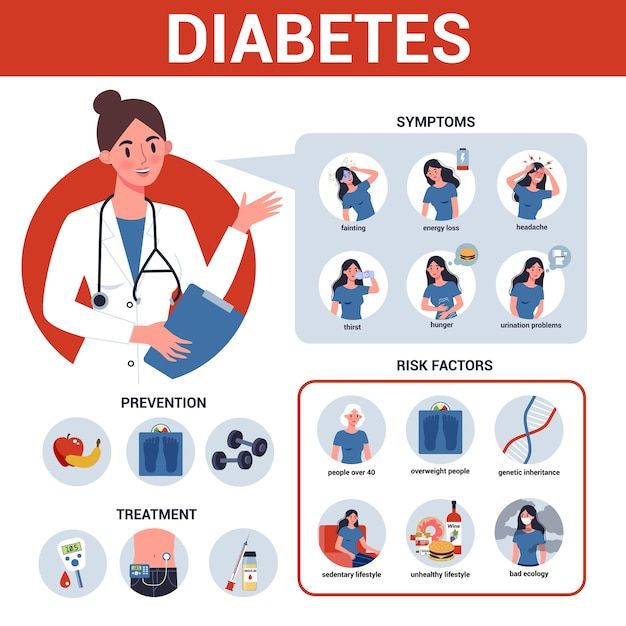
Factors Contributing to Diabetes
The factors that cause diabetes may depend on the type of diabetes. Some general factors, nonetheless, raise one’s chances of developing this disease:
Genetics: A family history of this disease can increase your chances of developing the condition.
Lifestyle Factors: A sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, and obesity can increase the risk of Type 2 diabetes.
Age: The risk of developing Type 2 increases with age, especially after 45.
Insulin Resistance: In Type 2, cells become resistant to insulin, leading to higher blood sugar levels.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Its symptoms vary depending on the type and extent of the condition. Some common this disease symptoms are:
- Excessive thirst and hunger
- Urinating a lot
- Fatigue
- Blurry vision
- Poor wound healing
- Unintended weight loss (in Type 1 diabetes)
If you have any of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek the advice of a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis.

Diagnosing
To diagnose this disease, physicians normally perform the following tests:
Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Checks blood sugar after at least 8 hours of fasting.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Checks blood sugar levels after consuming a sugary drink.
A1C Test: This test provides an average of your blood sugar levels over the past two to three months.
If your results indicate elevated blood sugar levels, your doctor will discuss further steps to manage the condition.
Types
1. Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children, adolescents, or young adults. It is caused by the immune system of the body attacking the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, making them unable to make insulin. Consequently, individuals with Type 1 diabetes have to receive insulin injections or an insulin pump to control their blood sugar levels.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is more prevalent than Type 1 and is frequently linked to lifestyle. In this form, the body either fails to produce adequate insulin or develops a resistance to it. Gradually, elevated blood sugar levels can harm organs and tissues and result in complications. Type 2 occurs more frequently among adults, though young people are increasingly being diagnosed.
3. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually disappears after giving birth. Women with gestational diabetes, however, are more likely to develop Type 2 in the future.
Controlling Diabetes Effectively
Controlling this disease requires changing lifestyle, medicines, and ongoing monitoring. Below are some major strategies to control this disease effectively:
1. Nutrition and Diet
Having a proper, balanced diet is crucial in controlling this disease Eat:
Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread
Fruits and vegetables: Opt for a variety of colorful, fiber-filled options
Lean proteins: Chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes
Healthy fats: Olive oil, avocados, and nuts
Steer clear of sugary foods and beverages, as they will bring on spikes in blood sugar.
2. Exercise Regularly
Exercise can help control blood sugar and overall health. Getting at least 30 minutes of moderate physical exercise, like walking, cycling, or swimming, can be a big help in controlling this disease.
3. Checking Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring your blood sugar level on a regular basis enables you to monitor how your body reacts to food, exercise, and medicine. Record your blood sugar results and discuss them with your doctor to help manage them more effectively.
4. Medications
Aside from lifestyle modification, certain individuals with this disease also require medication to manage their blood glucose levels. Insulin treatment is necessary for Type 1. Oral drugs or insulin injections are utilized by individuals with Type 2 based on their specific needs.
5. Stress Management
Cronic stress can increase blood glucose levels, making it more difficult to control this disease Engage in relaxation activities like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to minimize stress and enhance overall health.https://theechowriters.com/category/health-and-fitness/
The Place of Technology in Diabetes Care
Technology has in the last few years transformed this disease care. There are numerous devices and apps available, ranging from continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) to insulin pumps, which can assist one in monitoring his or her blood sugar levels and fine-tune treatment. They give real-time information, and thus more precise insulin dosing and improved control overall.
The Effect of Diabetes on Mental Well-being
Having this disease is emotionally and mentally demanding. Diabetics might feel anxious, depressed, or stressed because of the constant requirement to check blood sugar levels, take medications, and adopt changes in lifestyle. It is necessary to get help from mental health professionals and openly discuss any emotional issues you experience.
Complications of Untreated Diabetes
Diabetes, if not controlled, can cause serious complications. Some of the frequent complications are:
Cardiovascular diseases: Greater risk of heart disease and stroke.
Kidney damage (diabetic nephropathy): This disease can ultimately damage the kidneys.
Nerve damage (neuropathy): High blood sugar damages nerves, causing numbness or pain.
Retinopathy: Destruction of the blood vessels in the eyes, resulting in blindness.
Foot problems: Nerve damage and poor circulation cause foot ulcers and infection.
Follow-up appointments with your doctor and taking this disease under control will decrease the chance of such complications.https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/7104-diabetes
Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1 is impossible to prevent, but Type 2 may be prevented or postponed with dietary changes and an active lifestyle. The following tips can be taken for avoiding Type 2:
Reduce your weight: It is enough to lose even a small quantity of weight, as it lowers your risk for developing Type 2.
Exercise on a regular basis: At least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
Eat a healthy diet: Prioritize whole foods and cut down on processed sugars.
Stop smoking: Smoking can raise the risk of Type 2 as well as other health issues.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a condition that should not be taken lightly, but when managed well, individuals with this disease can lead full and healthy lives. Knowing the causes, signs, and efficient management techniques helps you take all the necessary actions to keep your health in order. Regular consultations, a well-balanced diet, exercise, and stress reduction are all necessary elements of managing diabetes.
If you or someone close to you is managing this disease it’s essential to closely collaborate with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan. Don’t be afraid to seek encouragement from friends, relatives, or a diabetes educator to keep you motivated and informed.
