Introduction
Food poisoning is a widespread yet dangerous condition of illness that results from the consumption of spoiled food or beverages. It results when poisonous bacteria, viruses, parasites, or toxins find their way into the digestive tract and cause stomach pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and other conditions.
In the following blog, we will be presenting causes, symptoms, types, prevention tips, and treatment for food poisoning.

What is food poisoning?
Food poisoning, or foodborne illness, is a stomach and intestinal infection or irritation caused by eating unsafe or contaminated food. It can occur in anyone regardless of age and can be mild or severe.
Causes
Its result when food or beverages are contaminated with pathogens (bacteria, viruses, or parasites). At times, toxic chemicals or spoiled food can also cause infection.
Common Causes Include:
- Bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria
- Viruses such as Norovirus and Hepatitis A
- Parasites such as Giardia and Toxoplasma
- Eating expired or undercooked food
- Drinking contaminated water
- Inadequate hygiene while handling foods
Symptoms of Food Poisoning
Symptoms of this disease usually appear within a few hours to a few days after eating contaminated food, varying based on the type of infection and the individual’s immune system.
Common Symptoms Are:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Stomach cramps
- Diarrhea
- Fever and chills
- Weakness and fatigue
- Headache
-
Types of Food Poisoning
There are a number of types of this disease due to various pathogens.
Bacterial:
- Salmonella (due to raw eggs and meat)
- E. coli (due to contaminated water and beef)
- Listeria (due to unpasteurized dairy products)
Viral:
- Norovirus (due to contaminated seafood and vegetables)
- Hepatitis A (due to infected food handlers)
Parasitic:
- Giardia (due to contaminated water)
- Toxoplasma (due to undercooked meat)
Risk Factors
Certain individuals are at greater risk of this disease because of their age, health status, or compromised immune system.
High-Risk Individuals Are:
- Pregnant women
- Infants and small children
- Older adults
- Persons with compromised immune systems
How is food poisoning diagnosed?
Physicians generally diagnose food poisoning from symptoms and the history of foods eaten recently. In serious cases, they can suggest stool exams, blood tests, or tests to determine the pathogen.
Treatment for Food Poisoning
Food poisoning in most cases subsides on its own within a few days. Severe dehydration or bacterial infection, however, needs medical treatment.
Home Remedies for Mild Cases:
- Drink water in abundance
- Rest and skip solid food
- Have electrolyte-rich beverages
- Have light food such as bananas, rice, and toast
Medical Treatment for Severe Cases:
- Antibiotics (for bacterial infection)
- Anti-nausea drugs
- IV fluids (for dehydration)
- Probiotics to replenish gut health
Complications of Food Poisoning
Severe this disease, if not treated, can cause serious health complications, including
- Dehydration
- Kidney failure
- Outbreaks of foodborne illness
- Compromised immune system
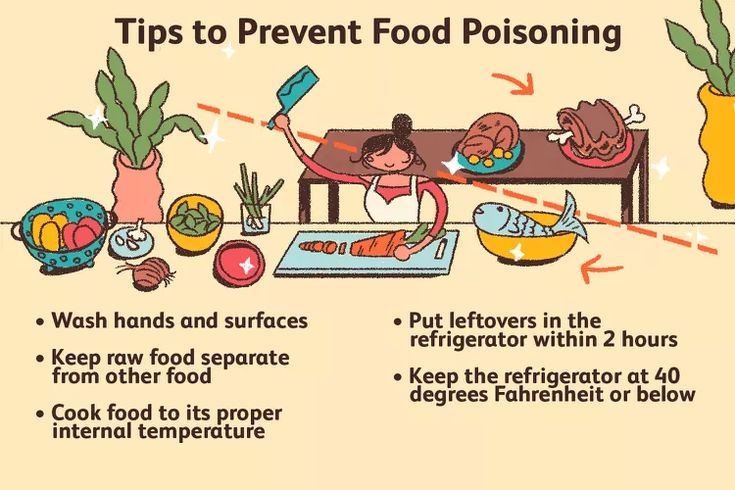
How to Avoid?
Practicing food safety can help minimize this disease risk.
Prevention Tips:
Wash your hands before handling and consuming food
Refrigerate food at the correct temperature
Do not consume raw or undercooked meat
Drink pure and filtered water
Do not consume street food and filthy restaurants
Best Foods to Recover from this disease
Foods to Consume:
- Plain toast and rice
- Banana and applesauce
- Herbal tea and coconut water
- Probiotic yogurt
Foods to Shun:
- Spicy and oily food
- Caffeinated beverages
- Alcohol and carbonated drinks
- Dairy products
How Long Does It Last?
The amount of time food poisoning lasts will vary depending on the type of infection and the individual’s immune system.
Mild cases: 24 to 48 hours
Moderate cases: 3 to 4 days
Severe cases: A week or longer https://theechowriters.com/category/health-and-fitness/
Myths and Facts About Food Poisoning
❓ Myth: Meat is the only food that can cause this disease.
✅ Fact: Fruits, vegetables, and even water can harbor harmful bacteria.
❓ Myth: Reheating food will destroy all bacteria.
✅ Fact: Certain toxins and bacteria can withstand hot temperatures.
Conclusion
Food poisoning is a prevalent and avoidable condition that arises through contaminated food and unhygienic habits. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21167-food-poisoning By adhering to correct food safety protocols, practicing hygiene, and being careful while consuming food outside, we can minimize the risk of infection.
In the event of extreme symptoms, it is crucial to obtain immediate medical attention to prevent complications.
